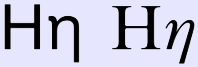|
|
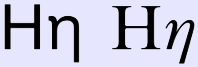
Eta (upper case Η, lower case η) is the seventh letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 8. The letter was pronounced like English long A (long E in most Continential European languages) in Ancient Greek.
Eta is sometimes used in place of eng (ŋ) when eng is not available, because of their similar appearance.
The upper-case letter Η is used as a symbol for:
- In textual criticism, the Alexandrian text-type (from Hesychius, its once-supposed editor).
- In chemistry, enthalpy.
The lower-case letter η is used as a symbol for:
- In thermodynamics, the efficiency of a Carnot heat engine.
- In chemistry, the number of electrons shared between a metal center and a ligand in a coordination compound. For example, an allyl group can coordinate to palladium in the η¹ mode or the η³ mode.
- In physics, the refractive index of an optical medium (although the letter n is used when Greek symbols are unavailable).
- In statistics, η2 is the "partial regression coefficient".
- In astronomy, the seventh brightest (usually) star in a constellation. See Bayer designation.
- In experimental particle physics, η stands for pseudorapidity
|
Ancient Greece
|
Medieval Greece / Byzantine Empire
|
Modern Greece
|
|
Science, Technology , Medicine , Warfare
, Biographies , Life , Cities/Places/Maps , Arts , Literature , Philosophy ,Olympics, Mythology , History , Images
|
Science, Technology, Arts
, Warfare , Literature, Biographies
Icons, History
|
Cities, Islands, Regions, Fauna/Flora ,
Biographies , History , Warfare
Science/Technology, Literature, Music , Arts , Film/Actors , Sport , Fashion
|
|
|