|
|
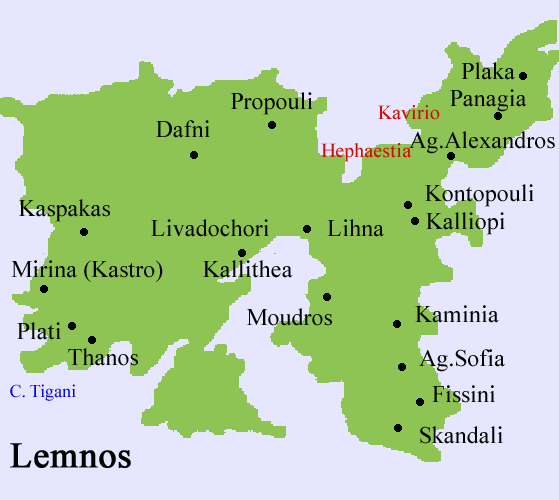
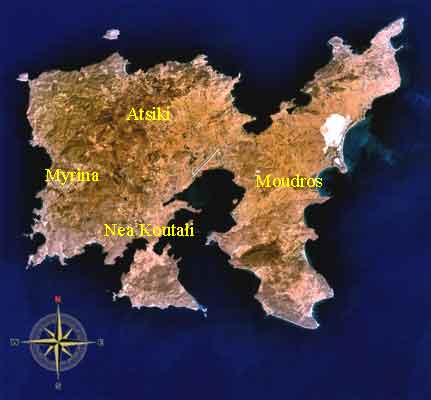
Nea Koutali (Νέα Κούταλη) is a village and a municipality on the island of Lemnos, in the Lesbos Prefecture, Greece. Population 2880 (2001). The seat of the municipality is in Kontias. Nea Koutali lies in the south central portion of the island, and with a land area of 75.735 km², covers about 15.9% of the island's area, the smallest of the four municipalities on Limnos. The municipal seat is the town of Kontiás (pop. 628 at 2001 census). Its next largest town is Néa Koútali (473).
* Alogonissi
Geography Its geography consists of almost entirely mountainous with several valleys, farmlands are in the valleys. History The village was built in 1926 in the area of Agia Marina, built by the refugees from a place formerly known as Koutali and been there since the Asia Minor Catastrophe. In its earliest years, it entered as a settlement of the community of Pesperago (now Pedino). In 1947, it became a part of the community of Nea Koutali in which it later became a municipal district in 1998, it received its municipal name and became a part of it. Along with Agios Dimitrios, it became the second village which was built by refugees from Asia Minor. Nea Koutali is built amphiteatrically by the Moudros Gulf. It stretches from a pine forests of Agia Triada which were planted by refugees and between the greatly cared houses with balconies which were with roses and geraniums, it features the stone built port filled with fishing boats. From all the villages of the island, Nea Koutali divides into a great plan. Interwar period In 1928, it had 351 inhabitants, it later ran a school with one inhabitant. It was built in 1930 and later roae to 70 students in 1938. It became a middle school in 1950s and in 1973, joined with the school of Neo Pedino and marked into a five grade school. Important works at school brought in sturdents, Isidoros Damals (1932-44), Iordanis Alevropoulos (1944-46), Stavroula Kratouni (1963-80), etc. The village was built with a same plan, it has trees and is named for the flower garden of its houses. It had 500 people in 1938 and had built 75 double buildings. Its residents continued to present that brought to the island and the most were learned with the sea as sailors, shipmen and others. Several were farmers. It had 15 sponge fishers in 1938, 50 divers and 700 oka fishers that amounted to 4 million drachmas. It had four oil machines, three ships with its passenger boats that performed everyday with the communications with the Moudros. From the port featured 160 annual departures. The difficulty of the time with the main halp brought from the USA, the Koutali Mutual Aid Council. Post-War period After World War II and the Greek Civil War, it was the few village in the island that kept its population, 457 in 1951 and 473 in 2001. It built its own gymnasium (secondary school) in 1980-89 and serves the villages of central Lemnos, the remainder are in Livadohori. Many sponge fishers that travels from all the Mediterranean. Koutalianoi brought them into Benghazi, Libya in 1963 for sponge fishing. One of these was known by the writer Giorgos Ioannou which used at the time in the Greek gymnasium - a daring diving that wrote in his journals Yia ena filotimo. The heroic of that time with the first fun of a family from Psara. About Nea Koutali and Economy As much as it have the inevitable assimilation with the older Limniots, the Koutalianoi had participated into the same importantce and their diacritics which characterizes the island. It has their presences. Its residdents with the gardens divides, brings in a different colour. The village shows its own kindergarten and public schools. It has fish taverns, unused bedrooms and runs its only rural plant. In recent yuears, several natural facilities and water by its bay along with its undepths salt marshes and a youth activity council around the soccer team Propontis in which it brought in distinction for several matches. Nea Koutali is well known in Greece and abroad for its sponge production. Until today, rans a clean sponge factory which produces throughout the world. It runs a machine for salt and organized units of production. It receives better food in Lemnis in several taverns. The Traditional Marine Museum On July 1, 2006, the Traditional and Sponge Marine Museum opened and featured the marine life of the Koutalians before they fled from Propontis, inside from the jewels and the archived photos from the old hometown, the diver's enjoyment. The museum is run by the Nea Koutali archeological council, it includes objects, even sponge from the depths of the sea and creates a large jar council, other ceramic stuff, ancient anchors and other small objects from the ancient marine. It features jars which dates back to the ancient and the Byzantine times. It originated from different parts of the Aegean and the Mediterrenean including Corinth, Chios, Thassos, Rhodes, Lesvos. It also originated from the Adriatic, Tarragon in northern Spain and Egypt. Sensational as the uses on the molydenum stuff from wooden anchors, as well as a sufficient number of signs with engraved from the Byzantine period. The running of the council occurred in the 1950s-1960s with the council with the member of the Nea Koutali Public School. Sources •"Portianou of Lemnos" by Costas Kontellis, 1998. •"Lemnos and its villages" by Th. Belitsos 1994. * Vasiliki Tourptsoglou-Stefanidou Adventurous And Geographic Features On Lemnos Island (15th to 20th Centuries) (Ταξιδιωτικά και γεωγραφικά κείμενα για τη νήσο Λήμνο (15ος-20ος αιώνας) = Taxidiotika ke geografika kimena gia ti niso Limno (15os-20os eonas) Thessaloniki 1986 Division of the municipality
Central Place, Church Agiou Ioanni Prodromou, War Memorial in Pedino (or Palaio Pedino "old Pedino")
Central Square, Church Agion Panton, War Memorial Neo Pedino ( "new Pedino") Koutali, Pedino and Agkaryones of Limnos from an inboard cameraof a Radio Controlled Airplane.
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
 |
||||||||||||||
|
|