|
|
Crowds of tourists climb the steps to the Propylaea, gateway to the Acropolis, Athens
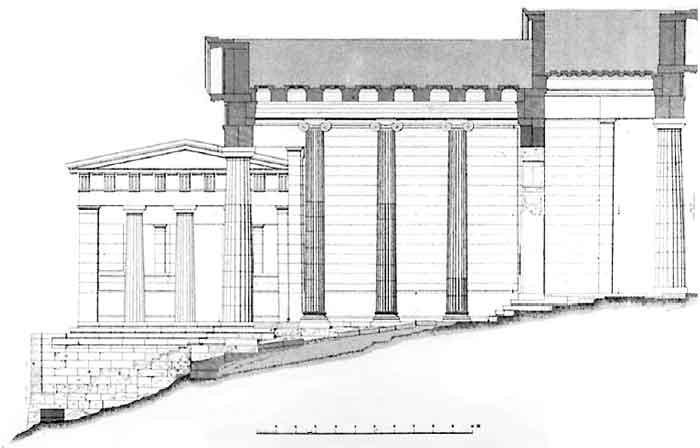
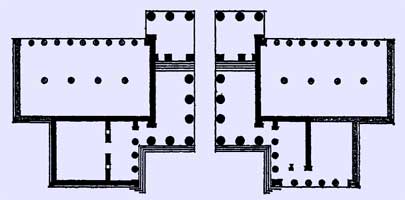
The Propylaea or Propylaia (Greek Προπυλαια) is the monumental gateway that serves as the entrance to the Acropolis in Athens. The word propylaia is the prefix pro (before or in front of) plus the plural of the Greek pylon or pylaion (gate), meaning literally that which is before the gates, but the word has come to mean simply gate building. The Propylaea was built under the general direction of the Athenian leader Pericles, but Pheidias was given the responsibility for planning the rebuilding the Acropolis as a whole at the conclusion of the Persian Wars. The building was designed by the architect Mnesicles. Construction began in 437 B.C.E. and was terminated in 431, when the building was still unfinished. The Propylaea was constructed of white Pentelic marble and gray Eleusinian marble or limestone, which was used only for accents. (Structural iron was also used, though William Bell Dinsmoor - "Structural Iron in Greek Architecture," American Journal of Archaeology, XXVI, 1922 - analyzed the structure and concluded that the iron weakened the building.) The structure consists of a central building with two adjoining wings on the west (outer) side, one to the north and one to the south. The core is the central building, which presents a standard six-columned Doric façade both on the West to those entering the Acropolis and on the east to those departing. The columns echo the proportions (not the size) of the columns of the Parthenon. The central building contains the gate wall (about two-thirds of the way through the central building). There are five gates in the wall, one for the central passageway, which was not paved and lay along the natural level of the ground, and two on either side at the level of the building. The central passageway was the culmination of the Sacred Way, which led to the Acropolis from Eleusis. Entrance into the Acropolis was controlled by the Propylaea. Though it was not built as a fortified structure, it was important that people not ritually clean be denied access to the sanctuary. In addition, runaway slaves and other miscreants could not be permitted into the sanctuary where they could claim the protection of the gods. The state treasury was also kept on the Acropolis, making its security important. The gate wall and the eastern (inner) portion of the building sit at a level five steps above the western portion, and the roof of the central building rose on the same line. The ceiling in the eastern part of the central building was famous in antiquity, having been called by Pausanias (about 600 years after the building was finished) ". . . down to the present day unrivalled." It consisted of marble blocks carved in the shape of ceiling coffers and painted blue with gold stars.
Stairs leading up to the Propylea The wings to the right and left of the central building stood on the same platform as the central building but were much smaller, not only in plan but in scale. Like the central building, the wings use Doric colonnades and Doric entablatures. However, the central building also has an Ionic colonnade on either side of the central passageway between the western (outer) Doric colonnade and the gate wall. This is therefore the first building known to us with Doric and Ionic colonnades visible at the same time. It is also the first monumental building in the classical period to be more complex than a simple rectangle or cylinder. The wing on the north (to the left as one enters the Acropolis) was famous in antiquity as the location of paintings of important Greek battles. Pausanias reports their presence, but few scholars believe the room was planned to hold them. Recent scholarship, following the lead of John Travlos (Pictorial Dictionary of Ancient Athens, New York, 1971), has taken the northern wing to have been a room for ritual dining. The evidence for that is the off-center doorway and the position near the entrance to the Acropolis. The wing on the south, though much smaller, was clearly designed to appear to be symmetrical. It seems only to have functioned as an access route to the Temple of Athena Nike. There were two wings planned for the east side of the Propylaea, facing in to the Acropolis. Preparations for both wings are apparent at the eastern end of the central building and along the side walls, but it seems that the plan for a southern wing was abandoned early in the construction process since the old fortification wall was not demolished, as required for that wing. The north wing was not built either. To the right of the Propylaea and further west, on the raised bastion prepared for it, stood the Temple of Athena Nike. As a result of the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta in 431 BC, the Propylaea was never completed. Not only are the eastern wings missing, the wall surfaces were not trimmed to their finished shapes, and lifting bosses remain on many blocks. The Propylaea survived intact through the Greek, Roman and Byzantine periods. During the period of Latin Empire, it served as the palace of the de la Roche family, who held the title Duke of Athens from 1204 to 1311. It was severely damaged by an explosion of a powder magazine in 1656. A tower of French or Ottoman date, erected on the south wing, was pulled down in 1874. Today the Propylaea has been partly restored, since 1984 under the direction of Dr Tasos Tanoulas, and serves as the main entrance to the Acropolis for the many thousands of tourists who visit the area every year. In the period before the 2004 Olympic Games in Athens, the Propylaia was shrouded in scaffolding as restoration work was undertaken. Mnesikles: The Propylaia and Kallikrates: the Nike Temple Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/"
|
|
|||||||||||||||||