|
|
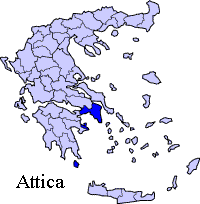
Periphery:Attica
Attica (in Greek: Αττική, Attikí) is a nomos (prefecture) in Greece, containing Athens, the capital of Greece. Attica is located in what is today southern Greece, and covers about 3,800 square kilometers. In addition to Athens, it contains within its area the cities of Piraeus, Eleusis, Megara, Laurium, and Marathon, as well as the islands of Salamis, Aegina, Poros, Hydra, Spetses, Kythira, and Antikythera. About 3,750,000 people live in the nomos, of which more than 95% are habitants of the Athens metropolitan area. Athens was originally the capital of Central Greece.
Geography Attica is a peninsula jutting into the Aegean Sea. Mountains divide the peninsula into the plains of Pedia, Mesogeia, and Thriasia. The mountains include Hymettus, the eastern portion of Geraneia, Parnitha, Aigaleo and the Penteli mountains. To the north it is bordered by the Boeotian plain and to the west it is bordered by Corinth. The Saronic Gulf lies to the south and the island of Euboea lies off the north coast. Athens' first and only large reservoir named Lake Marathon is about 35 km northeast and is called the Marathon Dam which first opened in the 1920s. Since that time, it is Attica's largest lake. Forests cover the area around Parnitha, around Hymettus and into the northeast and the north in the hills and the mountains except for the mountaintops but the mountains to the west and the south are grassy, barren or forested. The Cephisus River is the longest river, and Parnetha or Parnitha is the tallest mountain in Attica. The prefecture also has parklands in the Hymettus, Penteli and the Parnitha mountains and the southern part of the peninsula. According to Plato, Attica ancient boundaries were fixed by the Isthmus, and that in the direction of the continent they extended as far as the heights of Cithaeron and Parnes. The boundary line came down in the direction of the sea, having the district of Oropus on the right, and with the river Asopus as the limit on the left. Climate Its climate includes hot summers and cool to mild winters in low lying areas and its plains and most of the Saronic. Winter is very common in the mountains of Parintha and areas that lie 1,000 m above sea level at its lowest. In the winters of 1999 and February 2004, recent snowstorms plundered the area especially blocking and closing much of its roads as snow accumulated to 2 m.
History The process of how Attica was united by Athens is not entirely clear, but it concluded at some point in the first half of the 7th century BC when Eleusis and the surrounding plains were joined to the Athenian state, and its inhabitants became citizens. Even then, the boundaries were not fixed, as Athens struggled with Megara for control of Salamis, and with Boeotia over border towns like Oropus for centuries. See History of Athens. Attica later became part of (successively) the Roman and Byzantine Empires, the crusader Duchy of Athens, and the Ottoman Empire, until the Greek War of Independence.
Transportation
Roads and Highways The area is connected by roads and highways: Greece Interstate 1 (superhighway) Other Athens Mass Transit System Communications
Television Mega Channel - Athens
Hospitals Agios Panteleimonas Hospital - Nikaia
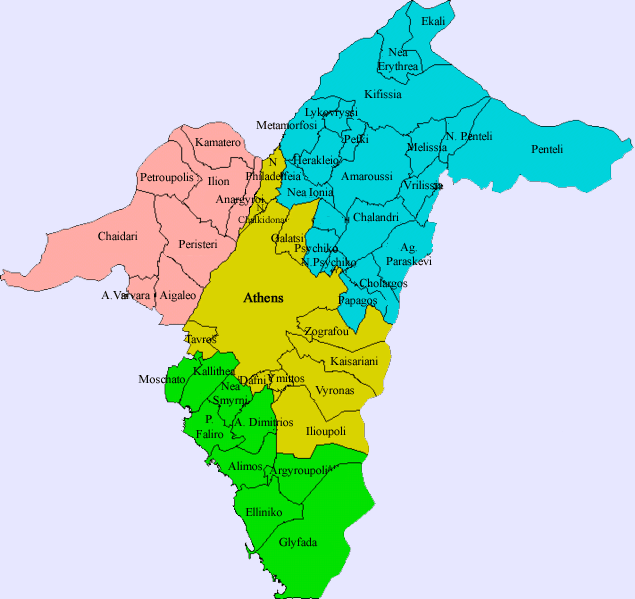
Municipalities List of municipalities of Attica
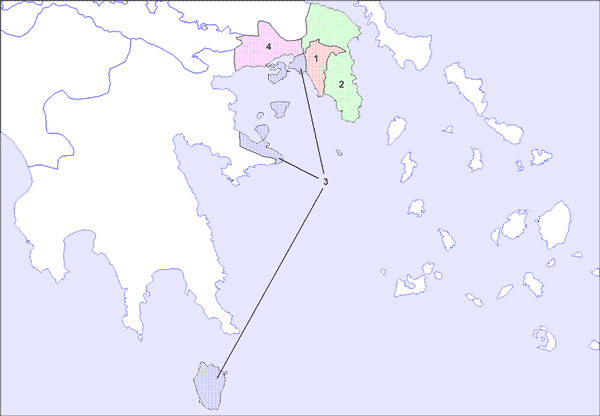
Prefectural sects of Attica (agglomeration)
The prefectures that make up the periphery of Attica include:
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org"
 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|